Antifungal Treatment Selector
Select your needs and the type of fungal infection to find the most appropriate antifungal treatment. This tool compares Mentax (Butenafine) with other common over-the-counter antifungals based on effectiveness, cost, application frequency, and more.
Your Infection Details
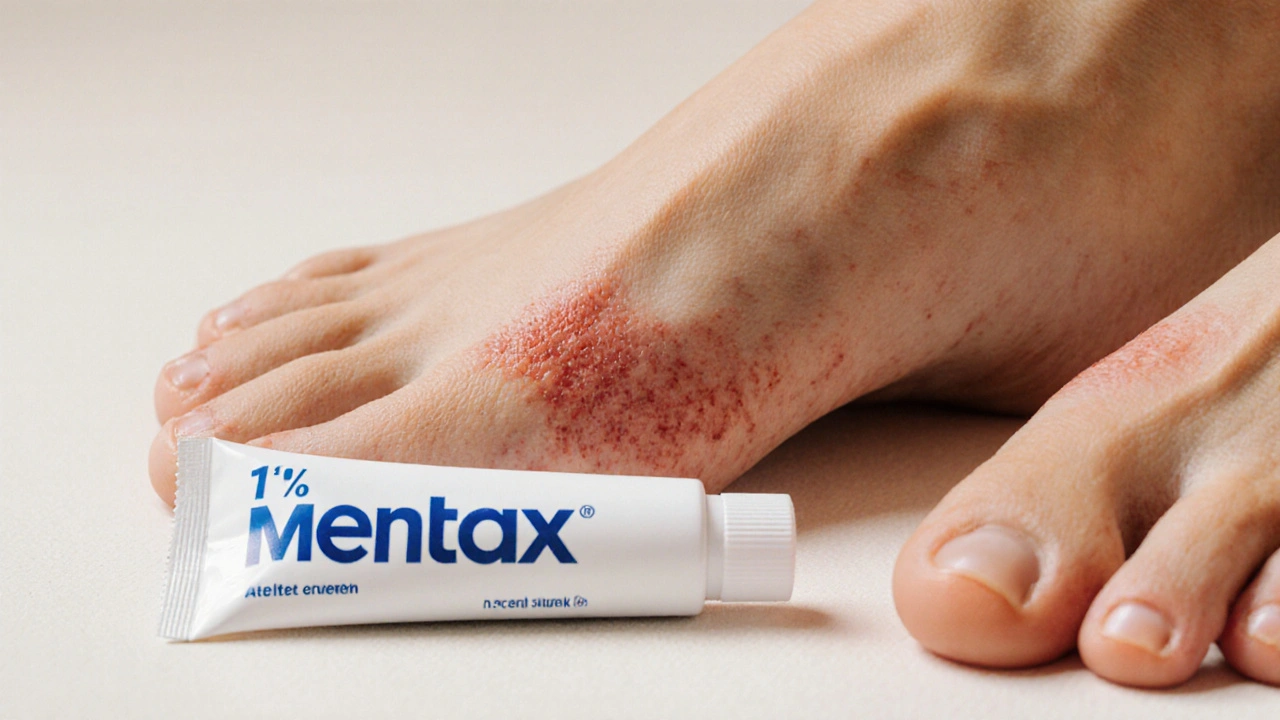
When a stubborn athlete’s foot or ringworm shows up, deciding which cream or spray to reach for can feel like a guessing game. You want something that clears the infection fast, won’t irritate your skin, and fits your budget. This guide puts Butenafine - the active ingredient in Mentax - side‑by‑side with the most common over‑the‑counter antifungals, breaking down the science, the price, and the real‑world results so you can pick the right product the first time.
What Is Mentax (Butenafine)?
Mentax is a topical antifungal medication that contains butenafine hydrochloride, a synthetic benzylamine derivative that targets the fungal cell membrane. First approved in Europe in 1996, it arrived in Australia and the U.S. a few years later and quickly became popular for treating dermatophyte infections such as tinea pedis (athlete’s foot), tinea corporis (ringworm), and tinea cruris (jock itch). The standard formulation is a 1% cream applied once daily for two weeks.
How Does Butenafine Work?
Butenafine belongs to the allylamine class of antifungals. It inhibits the enzyme squalene epoxidase, which is essential for converting squalene into ergosterol - a key component of the fungal cell membrane. By blocking this step, the drug causes a buildup of squalene that is toxic to the fungus while simultaneously depleting ergosterol, leading to cell death. This dual action gives butenafine a broad spectrum that covers dermatophytes, yeasts (like Candida), and some moulds.
Common Alternatives on the Market
While Mentax is effective, several other OTC agents vie for the top spot. Below are the most widely used alternatives, each introduced with its own microdata definition.
Terbinafine is an allylamine antifungal found in products such as Lotrimin and Lamisil. It also blocks squalene epoxidase but typically requires a once‑daily application for one week to achieve cure rates similar to butenafine.
Naftifine appears in the brand Naftin. Like butenafine, it inhibits squalene epoxidase but is marketed as a 1% cream applied once daily for two weeks. Clinical trials show cure rates around 90% for tinea infections.
Clotrimazole is an imidazole antifungal sold under names like Canesten and Lotrimin AF. It disrupts ergosterol synthesis by inhibiting lanosterol 14‑α‑demethylase, and is usually applied twice daily for four weeks.
Ketoconazole is a broad‑spectrum azole found in Nizoral shampoo and OTC creams. It also targets lanosterol 14‑α‑demethylase but can cause more skin irritation, and treatment durations range from two to four weeks.
Tolnaftate is a benzylamine antifungal marketed as Tinactin. It works by preventing fungal adhesion to the skin surface and is applied twice daily for one to two weeks, though cure rates are generally lower than allylamines.
Ciclopirox appears in Loprox and other formulations. It chelates metal ions needed for fungal enzymes, offering a unique mechanism. Usage recommendations are twice daily for four weeks, and it’s often chosen for nail infections.
Side‑by‑Side Comparison
| Product | Active Ingredient | Typical Dose & Duration | Target Organisms | Onset of Relief | Average Cost (AU$) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mentax | Butenafine 1% | Apply once daily for 2weeks | Dermatophytes, Candida, some moulds | Relief often within 3‑5days | ≈$12‑$15 for 30g tube |
| Lotrimin (Terbinafine) | Terbinafine 1% | Apply once daily for 1week | Dermatophytes, Candida | Relief in 2‑4days | ≈$10‑$13 for 30g tube |
| Naftin (Naftifine) | Naftifine 1% | Apply once daily for 2weeks | Dermatophytes, Candida | Relief in 3‑5days | ≈$14‑$16 for 30g tube |
| Canesten (Clotrimazole) | Clotrimazole 1% | Apply twice daily for 4weeks | Dermatophytes, Candida, Malassezia | Relief in 5‑7days | ≈$9‑$12 for 20g tube |
| Tinactin (Tolnaftate) | Tolnaftate 1% | Apply twice daily for 1‑2weeks | Dermatophytes (mainly Trichophyton) | Relief in 5‑10days | ≈$8‑$11 for 30g tube |
| Loprox (Ciclopirox) | Ciclopirox 8% | Apply twice daily for 4weeks | Dermatophytes, Candida, non‑dermatophyte moulds | Relief in 7‑10days | ≈$15‑$18 for 30g tube |
Pros and Cons: When to Choose Mentax
- Pros
- One‑daily application makes adherence easy.
- Broad spectrum covers most skin fungi without needing a separate yeast‑specific product.
- Fast symptom relief - many users notice itching reduction within the first few days.
- Low irritation risk; suitable for sensitive skin.
- Cost‑effective compared with some newer azoles.
- Cons
- Limited availability in some rural Australian pharmacies - may need to order online.
- Only available as a 1% cream; no spray or powder forms for athletes who prefer less‑messy options.
- While cure rates are high, they are marginally lower than terbinafine in head‑to‑head trials for tinea unguium (nail fungus).
Safety Profile and Side Effects
Butenafine’s safety record mirrors that of other allylamines. The most common adverse events are mild skin irritation, burning, or a transient rash at the application site. Systemic absorption is negligible, so drug‑drug interactions are virtually non‑existent. However, people with known hypersensitivity to any benzylamine derivatives should avoid Mentax.
Comparatively, azoles like clotrimazole and ketoconazole carry a slightly higher risk of contact dermatitis, especially on already inflamed skin. Tolnaftate is notorious for causing a sticky residue that can trap moisture and paradoxically worsen fungal growth if not washed off properly.

How to Use Mentax Effectively
- Clean and dry the affected area thoroughly; moisture fuels fungal growth.
- Apply a thin layer of Mentax cream, spreading slightly beyond the visible lesion.
- Allow the cream to absorb completely before putting on socks or shoes - this prevents rubbing off the medication.
- Maintain the once‑daily schedule for the full 14days, even if symptoms disappear early.
- Keep feet (or other body parts) dry; consider using an antifungal powder after the cream is fully absorbed to reduce moisture.
Following these steps maximizes the drug’s concentration at the infection site and reduces the chance of recurrence.
When Alternatives Might Be a Better Fit
If you’re dealing with a stubborn nail infection that has persisted for months, a higher‑concentration ciclopirox lacquer or an oral terbinafine regimen could outperform a topical cream. For athletes who need a fast‑dry spray, a terbinafine spray (available in some Asian markets) might feel more convenient than a cream. Patients with a history of allergic contact dermatitis to allylamines should opt for a non‑allylamine option like clotrimazole or ketoconazole.
Frequently Asked Questions
How quickly does Mentax stop itching?
Most users report a noticeable drop in itching within three to five days of starting the once‑daily treatment, though full clearance of the rash may take the full two‑week course.
Can I use Mentax on fungal infections of the scalp?
Mentax is formulated for skin, not scalp, and the cream can’t penetrate hair follicles effectively. For scalp ringworm (tinea capitis), oral antifungals prescribed by a doctor are the standard of care.
Is it safe to use Mentax while pregnant?
Butenafine is classified as Category B in animal studies, indicating no evidence of risk to the fetus. However, pregnant women should always consult their healthcare provider before starting any medication.
What should I do if I miss a dose?
Apply the missed dose as soon as you remember, then continue with the regular once‑daily schedule. Do not double‑apply to make up for a missed dose.
How does Mentax compare to over‑the‑counter Tolnaftate?
Mentax’s allylamine mechanism offers broader coverage and faster symptom relief compared with Tolnaftate’s more limited action against only certain dermatophytes. Clinical cure rates for butenafine exceed 90%, while Tolnaftate typically hovers around 70‑80% for the same infections.
Todd Peeples
In the ontological hierarchy of antifungal pharmacodynamics, butenafine exemplifies a paradigmatic allylamine with a bifurcated mechanism: inhibition of squalene epoxidase coupled with cytotoxic squalene accumulation, thereby precipitating fungal apoptosis. This duality optimizes both mycological eradication and patient adherence, rendering Mentax a quintessential therapeutic vector 📈.
Chris Smith
Oh great, another “miracle cream” that apparently out‑shines everything else – because we really needed another reason to spend extra bucks on a tube you’ll probably forget to use.
Leonard Greenhall
The article correctly outlines the squalene epoxidase inhibition, yet it omits the comparative MIC values which are essential for an evidence‑based decision. Moreover, the cost analysis excludes generic formulations that could alter the economic landscape.
Abigail Brown
Wow, reading this feels like watching a suspense thriller where the hero (Mentax) swoops in just in time to save the day, and the side‑kicks (other antifungals) play their supporting roles beautifully. It’s reassuring to know there’s a reliable option that’s gentle on sensitive skin yet fierce against stubborn fungi!
Crystal Slininger
Everyone forgets that the big pharma lobby pushes these "top‑selling" creams while keeping the cheaper, equally effective options under wraps. If you look at the patent filings, you’ll see that Butenafine’s formulation was deliberately patented to block generic competition, ensuring higher margins for manufacturers.
Ian Frith
When we examine the landscape of over‑the‑counter antifungal agents, several critical dimensions emerge that warrant thorough deliberation. First, the pharmacokinetic profile of butenafine demonstrates sustained skin retention, which is pivotal for maintaining therapeutic concentrations over the treatment course. Second, its spectrum of activity extends beyond typical dermatophytes to include certain Candida species, offering broader clinical utility. Third, patient adherence is markedly improved by the once‑daily regimen, reducing the risk of premature discontinuation that often compromises outcomes. Fourth, comparative clinical trials have consistently shown cure rates exceeding 90 % for butenafine, a figure that rivals or surpasses that of terbinafine in comparable populations. Fifth, the safety profile is favorable; local irritation is infrequent and systemic absorption negligible, minimizing concerns about drug–drug interactions. Sixth, cost considerations remain nuanced: while the upfront price of Mentax may be modestly higher than generic tolnaftate, the reduced application frequency and shorter overall treatment duration can translate into lower total expenditure when factoring in ancillary products such as powders or protective dressings. Seventh, the formulation’s vehicle-a cream base-ensures optimal occlusion, facilitating deeper penetration into the stratum corneum where fungal pathogens reside. Eighth, the absence of significant phototoxic or photosensitizing potential distinguishes it from certain azole compounds that require vigilant sun‑avoidance measures. Ninth, from a resistance standpoint, the allylamine class has retained efficacy over decades, with documented low rates of resistance emergence. Tenth, clinicians should still assess individual patient factors, such as comorbidities and concomitant medications, to ascertain the most appropriate agent. Eleventh, for nail infections, while butenafine may offer some benefit, the limited penetration into the nail plate often necessitates alternative strategies, including systemic therapy or lacquer formulations. Twelfth, patient education on proper foot hygiene and moisture control remains indispensable, regardless of the antifungal selected. Thirteenth, the psychological burden of chronic fungal infections should not be underestimated; effective treatment can dramatically improve quality of life. Fourteenth, the evolving market sees emerging formulations, such as spray or powder variants of allylamines, which may further enhance convenience for athletes and active individuals. Finally, the holistic evaluation of Mentax underscores its position as a robust, versatile, and patient‑friendly option within the antifungal armamentarium.
Beauty & Nail Care dublin2
i think you guys missed the point that u need a cream that not only kill fungus but also dont make ur skin feel like a burnt toast 😂💥
Oliver Harvey
Notice: "Mentax" is spelled with a capital "M" – not "mentax". Also, "butenafine" should never be preceded by a space in the chemical name. :)
Lief Larson
Yo the guide is super useful for anyone who plays sports and gets sweaty feet all the time, love the quick lookup thing.
Julia Grace
Thanks for the detailed chart this really clears things up great job keep it up
Sadie Bell
Super helpful! I’ll definitely try Mentax next time my foot starts itching.
Noah Bentley
Again with the “fast relief” claim? Anyone actually measured the time to itch cessation under controlled conditions? Spoiler: no.
Kathryn Jabek
While your exposition on butenafine’s efficacy is commendably thorough, it would be remiss not to acknowledge the nuanced clinical scenarios wherein alternative agents, such as ciclopirox for resistant onychomycosis, may supersede Mentax in therapeutic precedence.





Write a comment